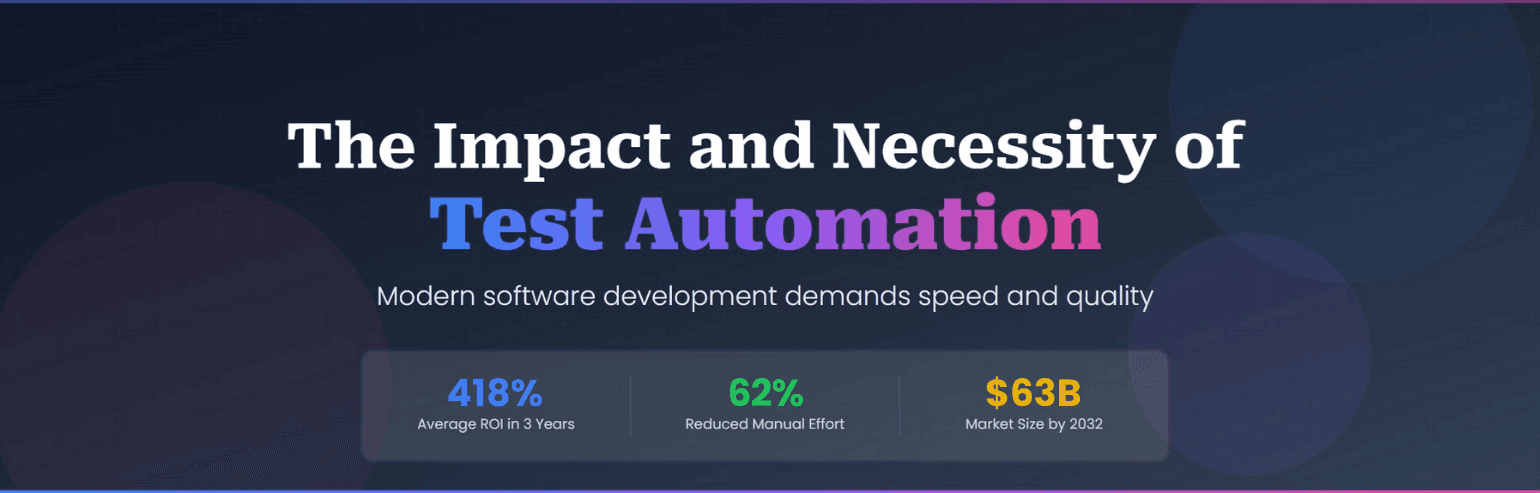
In the software development landscape, speed and quality are not just competitive advantages but survival requirements. As applications grow more complex and deployment cycles shrink from weeks to hours, manual testing alone cannot keep pace. Test automation has transformed from a good-to-have to an absolute necessity for teams serious about delivering reliable software quickly.
What is Test Automation?
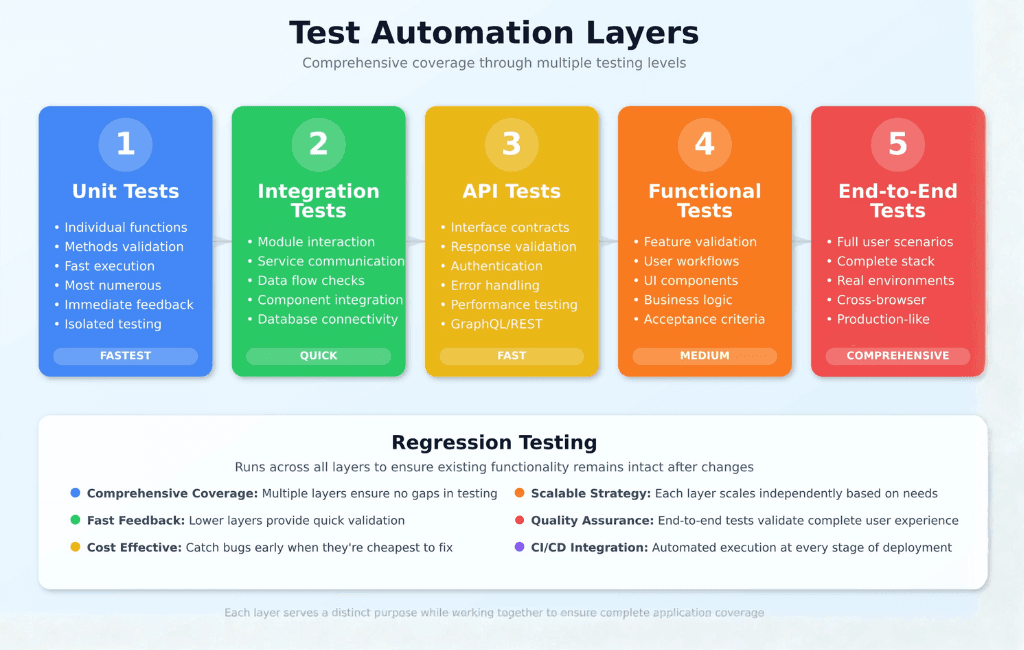
Test automation is the practice of using specialized software tools to execute pre-scripted tests on applications automatically. Unlike manual testing where QA engineers interact with software to verify functionality, automated tests run without human intervention, comparing actual results against expected outcomes, and generating comprehensive reports.
This approach covers multiple testing layers including unit tests, integration tests, API tests, functional tests, regression tests, and end-to-end tests. Each layer serves a distinct purpose in the quality assurance process, working together to ensure complete coverage across your application.
The Growing Market and Adoption
The test automation industry is experiencing explosive growth. According to recent market research by Fortune Business Insights, the global test automation market is projected to expand from $17.71 billion in 2024 to $63.05 billion by 2032, reflecting the increasing recognition of automation as a critical business investment rather than merely a technical tool.
Industry adoption rates support this trajectory. A Gartner survey of IT and software engineering leaders found that organizations commonly automate API testing and use automated testing continuously throughout the development cycle. Meanwhile, Forrester research estimates the testing services market at over $23 billion in 2023, growing steadily as more organizations embrace DevOps and continuous delivery practices.
Perhaps most tellingly, over 60% of companies report receiving positive ROI from their test automation investments, according to recent industry data. This demonstrates that when implemented strategically, automation delivers measurable business value that justifies the initial investment.
Why Test Automation is Essential Today
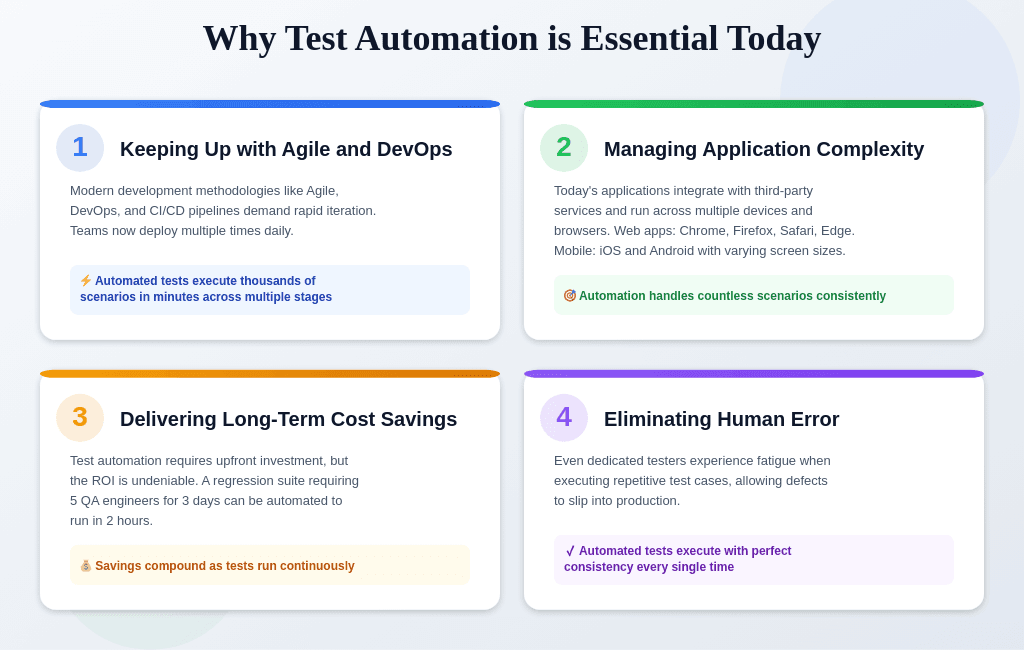
1. Keeping Up with Agile and DevOps
Modern development methodologies like Agile, DevOps, and CI/CD pipelines demand rapid iteration. Teams now deploy multiple times daily, making comprehensive manual testing impossible.
Automated tests execute thousands of scenarios in minutes. In CI/CD pipelines, tests run at multiple stages: unit tests during build, integration tests in staging, and smoke tests post-deployment. Without automation, teams must choose between speed and quality.
2. Managing Application Complexity
Today’s applications integrate with third-party services and run across multiple devices and browsers. Modern web apps must work across Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. Mobile apps need testing on iOS and Android with varying screen sizes and OS versions.
Automation handles these countless scenarios consistently, ensuring nothing slips through during releases.
3. Delivering Long-Term Cost Savings
Test automation requires upfront investment, but the ROI is undeniable. A regression suite requiring five QA engineers for three days to complete manually can be automated to run in two hours. Those engineers can then focus on exploratory testing and validating new features.
Over time, savings compound dramatically as tests run continuously without additional cost.
4. Eliminating Human Error
Even dedicated testers experience fatigue when executing repetitive test cases, allowing defects to slip into production. Automated tests execute with perfect consistency every time, ensuring core functionality remains intact across every release.
The Measurable Impact of Test Automation
Faster Time to Market
Organizations implementing robust test automation report significantly shorter release cycles. By automating regression testing, teams validate that new features have not broken existing functionality in hours instead of days.
This acceleration enables faster response to market demands, competitive pressures, and customer feedback. A 2023 Research Gate study on ROI in test automation found that enterprises achieved positive financial returns within 3.8 months of implementing automation, with an average three-year ROI of 418% across diverse industry implementations.
In competitive markets, this speed advantage often determines market leadership. Organizations using automation can deploy updates multiple times daily, whereas those relying on manual testing struggle to maintain weekly release schedules.
Expanded Test Coverage
Automation enables execution of far more test cases than manual testing allows. Comprehensive coverage across different browsers, operating systems, devices, and user scenarios becomes achievable rather than aspirational.
Additionally, automated tests can run overnight or during off-hours, maximizing resource utilization without requiring 24/7 human staffing. Teams arrive each morning with fresh insights about application health.
Improved Software Quality
Test automation’s ultimate goal is delivering high-quality software. By catching defects early in the development lifecycle, teams address issues when they are least expensive to fix, preventing problems from compounding and reducing critical production incidents.
Consistent automated testing also builds application stability over time. Teams gain confidence that core functionality remains solid, creating a stable foundation for new development.
Better Team Productivity
Automation frees skilled QA engineers from repetitive tasks, allowing them to focus on activities requiring human judgment: exploratory testing, usability evaluation, complex scenario validation, and test strategy development.
According to Capgemini’s World Quality Report, 69% of organizations feel they consistently meet their quality goals when leveraging automation effectively. Furthermore, research shows that automated testing can reduce manual testing effort by 62% while decreasing regression testing costs by 45%.
Development teams benefit too. Instead of waiting days for manual test results, developers receive immediate notification when their code impacts existing functionality, enabling quick fixes before issues escalate.
Critical Success Factors for Test Automation
Selecting the Right Tests to Automate
Not every test deserves automation. The best candidates are:
- Tests that run frequently (regression suites, smoke tests)
- Time-consuming manual test cases
- Tests requiring execution across multiple configurations
- Critical business workflow validations
- Data-driven tests with multiple input combinations
Poor automation candidates include:
- Tests that change frequently with requirements
- One-time exploratory scenarios
- Tests requiring subjective human judgment (visual design, UX feel)
- Edge cases with minimal business impact
Choosing Appropriate Tools
The test automation ecosystem offers numerous solutions, from open-source frameworks like Selenium, Cypress, and Playwright to commercial platforms with advanced capabilities.
Your choice depends on:
- Application type (web, mobile, desktop, API)
- Technology stack and languages
- Team expertise and learning curve
- Budget constraints
- Integration requirements with CI/CD pipelines
- Support and community resources
For end-to-end test automation specifically, you need tools capable of simulating real user journeys across your entire application stack, including cross-browser testing, parallel execution, visual regression detection, and seamless CI/CD integration.
Building Maintainable Test Suites
Poorly architected automated tests become maintenance nightmares, consuming more effort than they save. Successful automation requires:
Good practices:
- Clear test organization and naming conventions
- Reusable components and helper functions
- Proper separation of test data from test logic
- Comprehensive error handling and reporting
- Clear documentation for team knowledge sharing
- Regular refactoring to eliminate duplication
Maintenance considerations:
- Tests must evolve with the application
- UI changes require test updates
- Regular review and cleanup of obsolete tests
- Flaky tests should be fixed immediately, not ignored
Common Test Automation Challenges
Initial Investment Requirements
Setting up automation infrastructure requires time, budget, and expertise. Teams need to evaluate tools, establish frameworks, create test environments, and train team members.
A Gartner survey identified high upfront costs (34%), implementation struggles (36%), and automation skill gaps (34%) as the most significant challenges organizations face when deploying automated testing. These hurdles can seem daunting, particularly for smaller teams or organizations new to automation.
However, viewing this as pure cost misses the bigger picture. It is an investment that pays dividends through faster releases, reduced manual testing costs, and improved software quality. Organizations that successfully navigate the initial setup phase typically see returns within the first year.
Test Maintenance Overhead
Applications evolve constantly, and tests must keep pace. Frequent application changes can lead to test maintenance becoming a significant burden if not properly managed.
Common maintenance challenges include:
Brittle locators: Tests relying on fragile CSS selectors or XPath break when UI elements change. Use stable locators based on data attributes like data-testid for resilience.
Hard-coded waits: Fixed sleep() statements make tests slower and unreliable. Replace with explicit waits that poll for specific conditions.
Test interdependencies: Tests depending on execution order or shared state create fragile suites. Each test should run independently in isolation.
Mitigate through good architecture: use page object patterns, create abstraction layers, avoid brittle locators, and make tests resilient to minor UI changes.
Managing False Positives
Flaky tests that intermittently fail without application defects undermine automation confidence. They create noise, waste investigation time, and cause teams to ignore legitimate failures.
Common causes include:
Race conditions: Asynchronous operations completing unpredictably. Use explicit waits for specific conditions.
Network latency: Variable API call timing. Implement retry mechanisms with exponential backoff.
Test pollution: Tests affecting each other through shared state. Ensure proper cleanup in teardown methods.
Address flakiness immediately through proper synchronization, stable test data, isolated environments, and robust error handling. A flaky test suite is worse than no automation at all.
The Future of Test Automation
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are revolutionizing test automation. Emerging capabilities include:
AI-powered test generation analyzes application behavior and automatically creates relevant test cases. Tools use machine learning to understand user flows, identify critical paths, and generate test scripts that cover common scenarios.
Self-healing tests that adapt to minor UI changes without manual updates, reducing maintenance overhead. When a locator fails, AI algorithms try alternative strategies to find the element based on context, position, or visual appearance.
Intelligent test prioritization predicts which tests are most likely to catch issues based on code changes. Machine learning models analyze code commits, historical failure patterns, and coverage data to run the most relevant tests first.
Visual AI testing that understands visual context like a human tester, catching UI issues that code-based assertions miss. Computer vision algorithms detect layout problems, alignment issues, color inconsistencies, and rendering bugs across different browsers and devices.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables writing tests in plain English that get automatically converted to executable code, lowering the technical barrier for test creation.
As software continues driving business success, test automation will only grow more critical. Organizations investing in robust automation strategies today position themselves as tomorrow’s quality leaders.
Conclusion
Test automation is not optional anymore but fundamental for modern software development. Its impact extends beyond QA teams, influencing development velocity, product quality, resource efficiency, and ultimately business success.
The benefits are clear: faster releases, reduced costs, improved quality, and better team productivity. While implementation requires investment and discipline, organizations that master test automation gain significant competitive advantages.
Whether you’re starting your automation journey or enhancing existing capabilities, focus on building maintainable test suites, choosing appropriate tools, and fostering a quality-first culture. The teams that excel at test automation today will define the quality standards of tomorrow.
Ready to transform your testing approach? Start with one critical workflow, prove the value, and expand from there. Your future self will thank you.